In the world of temperature measurement, accuracy is paramount. To achieve precise readings in various environments, one must consider the type of cable used. Compensating cables, also referred to as thermocouple cables, are the unsung heroes of temperature measurement.
They come in various forms, each tailored to specific applications and temperature ranges. In this comprehensive guide for CAP IT products, we will delve into four common types of compensating cables: compensated cables (Tx, Jx, Kx, Nx), fiberglass, PVC, and PFA. Let’s explore the nuances of each to help you make an informed choice for your temperature monitoring needs.
Compensating cables (Tx, Jx, Kx, Nx)
Fiberglass
Application: These cables are engineered for use in high-temperature environments and possess exceptional fire resistance capabilities.
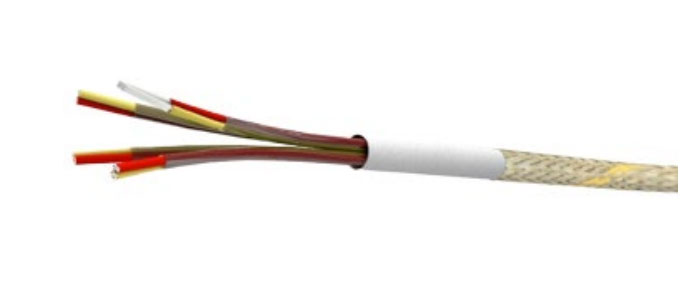
Construction
Conductor: The conductor can be either solid or flexible, offering versatility in installations.
Insulation: The insulation material used here is a braided fiberglass, which is available in two variants: “E” or “R/S” (spiral fiberglass is also available).
Coupling: Stranded conductors are coupled with a fiberglass filler.
Inner layer: A braided fiberglass inner layer, again, in “E” or “R/S” variants.
Impregnation Method: Silicone liquid or varnish is used for impregnation.
Outer Armor: The cable is protected with a galvanized steel braid.
Operating Temperature: These cables can handle temperatures of up to +400°C for “E” type and +650°C for “R/S” type (HT).Insulation Electrical Resistance: With a measurement of >20 Mohm x km (measured at 1000 Volt dc @ 20 °C), these cables ensure reliable electrical performance.
PVC
Application: PVC compensating cables are well-suited for applications where temperatures range from 80-105°C and exposure to chemicals is expected. They are particularly useful for thermocouples like type T, J, N, and K.

Construction
Conductor: Similar to other types, you can opt for either solid or flexible conductors.
Insulation: PVC is used as the insulation material (or alternatively, XLPE or HEPR).
Coupling: Stranded conductors are employed.
Intermediate Sheath: A PVC intermediate sheath is utilized, often made of LS0H (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) material.
Armor: Galvanized steel wire braid provides mechanical protection.
Outer Sheath: The cable is enclosed with a PVC sheath (or LS0H).
Operating Temperature: PVC compensating cables can handle temperatures ranging from -30 to 80°C (105°C).
PFA
Application: PFA compensating cables are the go-to choice when dealing with extreme conditions, including temperatures up to 260°C and exposure to harsh chemicals.

Construction
Conductor: Like other types, PFA compensating cables come with the option of solid or flexible conductors.
Insulation: PFA is used for insulation.
Coupling: Stranded conductors are employed.
Separator: A polyester tape acts as a separator.
Shielding: These cables are shielded with aluminum-polyester tape and feature a tinned copper drain wire.
Outer Sheath: The outer sheath is composed of PFA.
Operating Temperature: PFA compensating cables can handle temperatures ranging from -200 to 260°C.
Insulation Electrical Resistance: Their insulation boasts an impressive >20 Mohm x km (measured at 1000 Volt dc @ 20 °C).
PVC
Application: Designed as extension cables for TC S and B thermocouples, PVC compensating cables are suitable for temperature ranges up to 80-105°C and chemical exposure.

Construction
Conductor: As with other types, you can choose between solid or flexible conductors.
Insulation: PVC is used for insulation (or alternatively, XLPE or HEPR).
Coupling: Stranded conductors are employed.
OuterSheath: The cable is enclosed with a PVC sheath (or LS0H).
In summary, selecting the appropriate compensating cable is pivotal to ensure the accuracy of temperature measurements and the overall success of your applications. Each cable type has its unique strengths, making it suitable for specific scenarios.
By considering factors such as temperature range, environmental conditions, and the presence of chemicals, you can make an informed choice to meet your temperature monitoring needs effectively.
Whether you require high-temperature resistance, chemical resistance, or specific mechanical properties, there’s a compensating cable tailored to your requirements.
Browse the catalogue to learn more!


